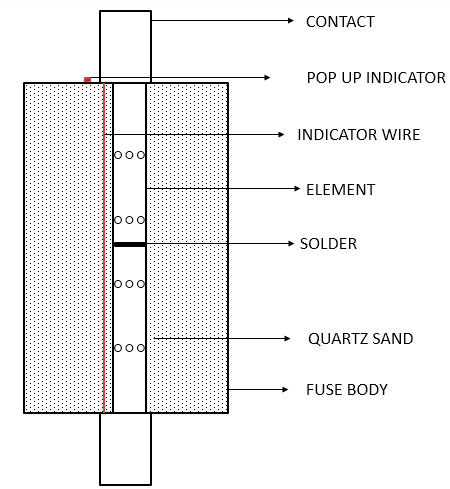
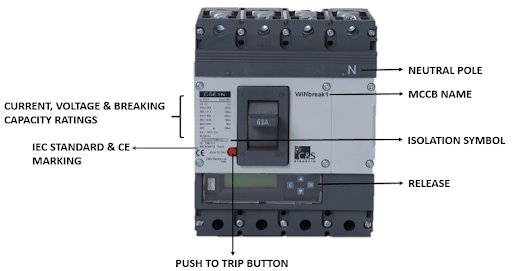
A circuit breaker is a switching device which can be operated manually and automatically for control and protection of electrical power circuit.
The primary purpose of a circuit breaker is to protect the system from the damage in series connected equipment & to minimize the area of damage and to minimum duration of power loss. However the first consideration in the discrimination is the correct circuit sizing breaker of main and branch breaker.
Discrimination is the coordination between the operating characteristics of circuit breakers placed in series. When the fault occurs in system only the circuit breaker placed immediately upstream of the fault will trip.
Discrimination as per IEC 60947-2 can be defined as follows:
- The total discrimination: This is a type of current based discrimination where in there are two circuit breakers in series, the circuit breaker on the load side effects the protection without causing the upstream circuit breaker to operate/trip
- Partial Discrimination: This is a type of current based discrimination where in there are two circuit breakers in series, the circuit breaker on the load side effects the protection up to a defined level of overcurrent, without causing the upstream circuit breaker to operate/trip.
Principles of discriminative tripping (selectivity)
Discrimination may be total or partial, and based on the principles of current levels, or time-delays, or a combination of both. A more recent development is based on the logic techniques Discrimination is achieved by automatic protective devices if a fault condition, occurring at any point in the installation, is cleared by the protective device located immediately Upstream of the fault, while all other protective devices remain unaffected.
- Protection against overload: discrimination based on current levels
This method is realized by setting successive tripping thresholds at stepped levels, from downstream relays (lower settings) towards the source (higher settings). Discrimination is total or partial, depending on particular conditions, as noted above. - Protection against low level short-circuit currents: discrimination based on stepped time delays
This method is implemented by adjusting the time-delayed tripping units, such that downstream circuit breakers have the shortest operating times, with progressively longer delays towards the source.
Current-level discrimination – Principle
Current-level discrimination is achieved with stepped current-level settings of the instantaneous magnetic-trip elements. Current-level discrimination is achieved with circuit breakers, preferably current limiting, and stepped current-level settings of the instantaneous magnetic-trip elements.
The downstream circuit-breaker is not a current-limiter device
Total discrimination in this situation is practically impossible because
Isc A ≈ Isc B, so that both circuit-breakers will generally trip simultaneously. In this case discrimination is partial, and limited to the Im of the upstream circuit-breaker.
The downstream circuit-breaker is a current-limiting device. Improvement in discriminative tripping can be obtained by using a current limiter for circuit-breaker B. For a short-circuit downstream of B, the limited level of peak current IB would operate the (suitably adjusted) magnetic trip unit of B, but would be insufficient to cause circuit-breaker A to trip.
Time-based discrimination- Principle
This technique requires:
The introduction of time-delays into the tripping mechanisms of circuit breakers
Circuit Breakers with adequate thermal and mechanical withstand capabilities at the high current levels and time delays considered Two circuit-breakers A and B in series (i.e. carrying the same current) are discriminative if the current-breaking period of downstream circuit-breaker B is less than the non-tripping time of circuit-breaker A
C&S offers total discrimination up to fault level of 50kA. For total discrimination, the customers can select Winmaster2 Air Circuit Breakers (ACBs) & Winbreak2 Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs). Customers can refer selection of up- stream and down-steam breaker details (kA, Rating & AF) from the selection tables provided by C&S Electric.